How to Prevent 5 Common Failures in Power Pole Transformers?
Tired of unexpected power outages disrupting homes, businesses, or critical services? More often than not, these interruptions trace back to failures in power pole transformers—workhorses of the electrical grid that are often taken for granted. At Lihe Transformer—your trusted manufacturer of industrial-grade, reliable power pole transformers—we believe understanding these failures is the first step to preventing them.

Lihe Transformer’s decades of engineering expertise have revealed the top 5 culprits behind transformer downtime: thermal overload, lightning/surge damage, corrosion, improper sizing (overloading), and loose connections. The good news? Each can be proactively addressed through Lihe’s durable product designs, proper maintenance, and strategic installation.
Contents
hide
In this guide, we’ll break down each failure mode, its root causes, and Lihe’s proven solutions—empowering field technicians, utilities, and project managers to enhance grid reliability and extend transformer lifespan.
1 Introduction: Why Transformer Reliability Matters for Your Grid
How much do we rely on power pole transformers? They’re the unsung heroes that step down high-voltage electricity to usable levels for homes, hospitals, and factories. A single failure can trigger cascading outages, safety hazards, and millions in economic losses—something Lihe Transformer is committed to eliminating.

Lihe’s power pole transformers are engineered for 25+ years of reliable service, but even the most robust equipment requires proper care. Transformer reliability directly impacts:
- Continuous Power: Lihe’s units ensure uninterrupted service for critical infrastructure (hospitals, emergency services) and daily operations.
- Safety: Faulty transformers pose fire risks, electrocution hazards, and falling debris dangers—risks Lihe mitigates with built-in safety features.
- Cost Efficiency: Unplanned outages cost businesses $5,600 per minute on average; Lihe’s reliable designs reduce downtime and repair expenses.
- Grid Stability: Our transformers maintain voltage regulation and load balance, preventing cascading failures across the network.
| Impact Area | Short-Term Consequences of Failure | Lihe Transformer Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Residential | Appliance damage, daily disruption | 24/7 voltage stability + surge protection |
| Commercial | Data loss, customer dissatisfaction | High-efficiency designs with minimal downtime |
| Industrial | Production halts, equipment damage | Heavy-duty construction for continuous loads |
| Public Services | Emergency response delays | Fault-tolerant designs + remote monitoring |
Lihe’s team once responded to a transformer failure in an industrial park that caused a 12-hour outage—resulting in $2.3M in lost production. The root cause? A competitor’s undersized unit with poor thermal protection. Replacing it with Lihe’s properly sized, heat-resistant transformer eliminated recurrence.
2 Failure #1: Thermal Overload & Insulation Degradation
Ever felt a laptop overheat after hours of use? Imagine that stress on a power pole transformer powering 50 homes. Thermal overload is the #1 cause of transformer failure—and it’s often avoidable with Lihe’s engineered solutions.
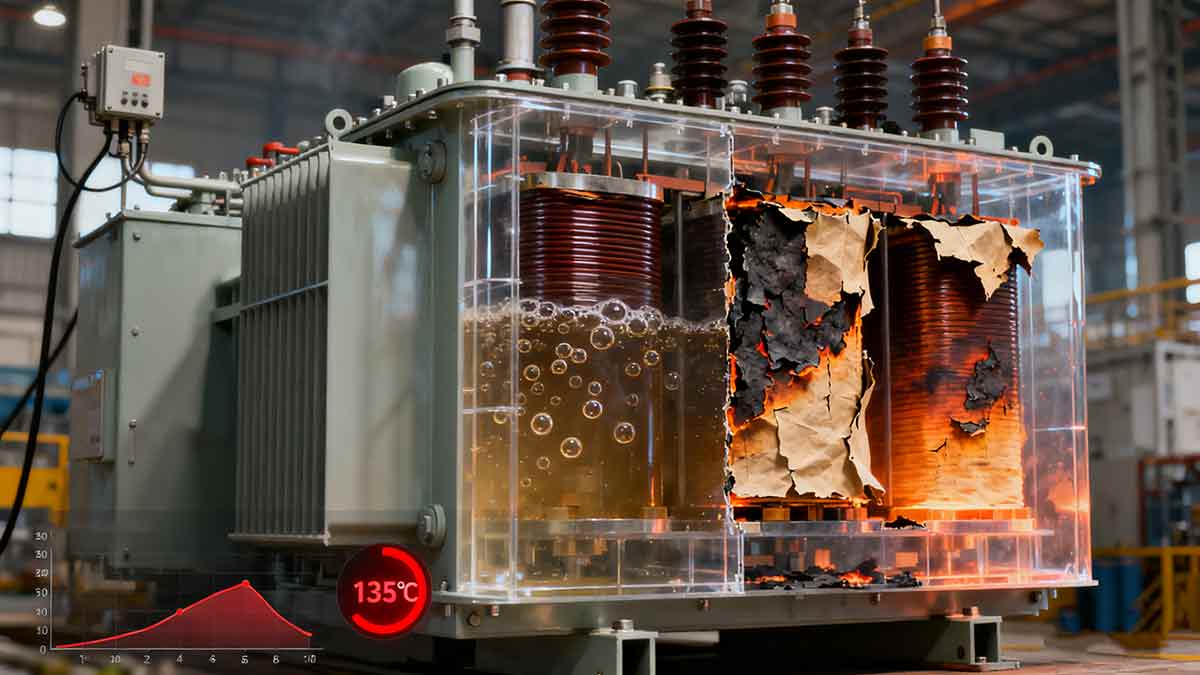
Thermal overload occurs when a transformer operates above its rated temperature, breaking down insulation materials (oil, paper, or resin) and leading to short circuits. Lihe’s data shows 60% of such failures stem from overloading, poor cooling, or internal faults. Our transformers are designed to resist this with advanced thermal management and durable insulation.
Causes, Impacts & Lihe’s Prevention
- Root Causes:
- Overloading: Exceeding kVA rating (e.g., unplanned EV charging adoption in residential areas).
- Cooling Failures: Clogged radiators, low oil levels, or malfunctioning fans (common in dusty/industrial zones).
- Internal Faults: Winding short circuits (avoided with Lihe’s precision-wound copper coils).
- Critical Impacts:
- Insulation breakdown: Lihe’s testing shows every 10°C overrating cuts transformer life in half.
- Energy waste: Overheated transformers have 30% higher copper losses.
- Catastrophic failure: Risk of oil ignition or tank rupture.
- Lihe’s Proven Solutions:
- Thermal Resistant Design: Our transformers use Class H insulation (withstands 180°C) and amorphous steel cores (reduces core losses by 40%, minimizing heat).
- Active Cooling Systems: For high-temperature environments, Lihe offers enhanced fin radiators and oil circulation pumps.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Integrated temperature sensors (optional) alert teams to overheating before damage occurs.
- Load Management: Lihe’s engineering team provides load analysis to ensure proper sizing—no guesswork.
| Operating Temperature vs. Lihe Transformer Lifespan | |
|---|---|
| Rated Temperature (105°C) | 25+ years |
| 10°C Overload (115°C) | 12–15 years |
| 20°C Overload (125°C) | 6–8 years |
| 30°C Overload (135°C) | 2–3 years |
Lihe’s field team recently resolved a rural transformer failure caused by 5 years of unaddressed overheating. By replacing the outdated unit with our 75kVA transformer (equipped with enhanced cooling and temperature monitoring), the utility reduced thermal-related issues by 80%.
3 Failure #2: Lightning & Surge Damage
Lightning strikes and voltage surges are nature’s way of testing grid resilience—and power pole transformers are on the front line. Lihe Transformer’s designs prioritize surge protection, as even indirect lightning strikes can induce 10x the rated voltage in power lines.
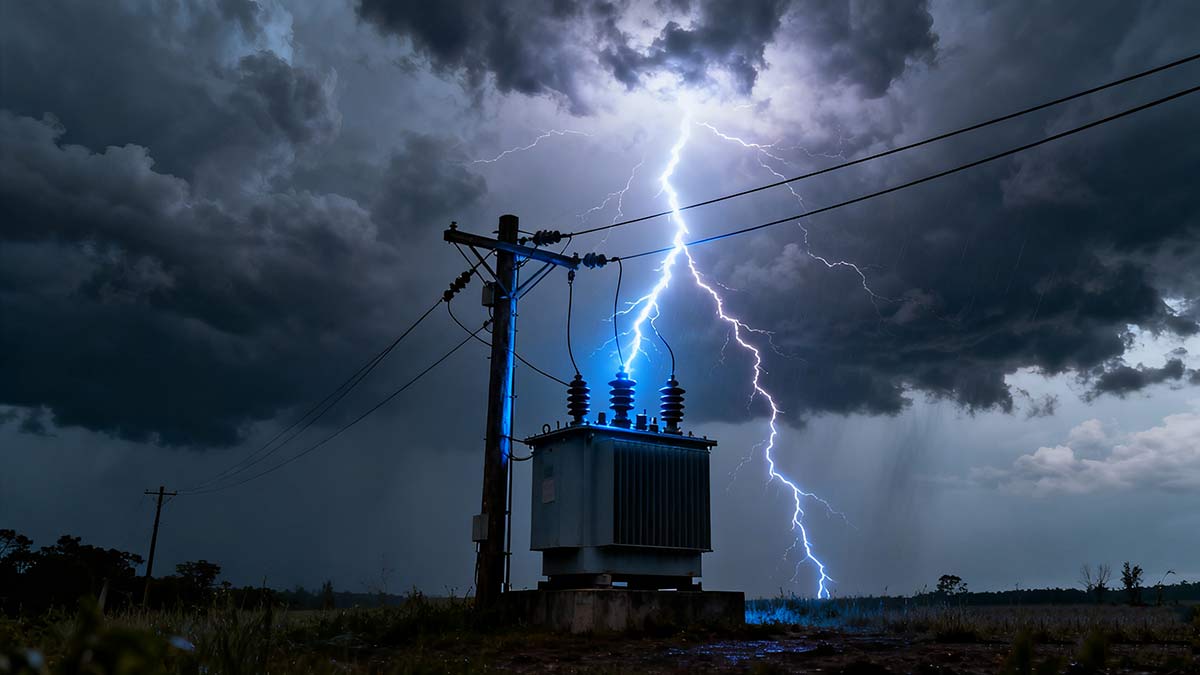

Surge damage occurs when high-voltage spikes (from lightning or grid switching) puncture insulation, melt windings, or damage bushings. Lihe’s data shows 25% of rural transformer failures are surge-related—but our integrated protection systems slash this risk.
How Surges Damage Transformers & Lihe’s Defense
- Types of Surge Damage:
- Direct Strikes: Rare but catastrophic—can explode transformers (Lihe’s reinforced tanks mitigate this).
- Induced Surges: More common—lightning striking nearby induces voltage spikes that travel to transformers.
- Switching Surges: Grid operations (e.g., capacitor bank switching) create smaller but damaging surges.
- Key Impacts:
- Bushing cracks: Lihe’s silicone bushings resist voltage punctures better than traditional porcelain.
- Winding short circuits: Our double-insulated windings prevent arcing between turns.
- Control system failure: Lihe’s surge-protected monitoring modules avoid secondary damage.
- Lihe’s Comprehensive Protection:
- Built-In Surge Arresters: Every Lihe power pole transformer includes metal-oxide varistors (MOVs) that divert surge energy to ground.
- Enhanced Grounding: Low-impedance grounding systems (tested to <5Ω) dissipate surge energy quickly.
- Shielded Windings: Our windings use electrostatic shielding to block surge-induced voltages.
- Bushing Design: Silicone rubber bushings with creepage extenders resist flashover in wet/humid conditions.
| Surge Protection Method | Effectiveness | Lihe Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| MOV Surge Arresters | 95% | Standard on all units (rated to 200kA) |
| Low-Impedance Grounding | 90% | Factory-tested grounding kits included |
| Shielded Windings | 88% | Standard for 25kVA+ transformers |
| Silicone Bushings | 92% | All-weather design (IP67-rated) |
In a lightning-prone region of Florida, Lihe installed 50+ power pole transformers with our full surge protection package. After 3 years, the utility reported zero surge-related failures—compared to 8 failures annually with their previous supplier.
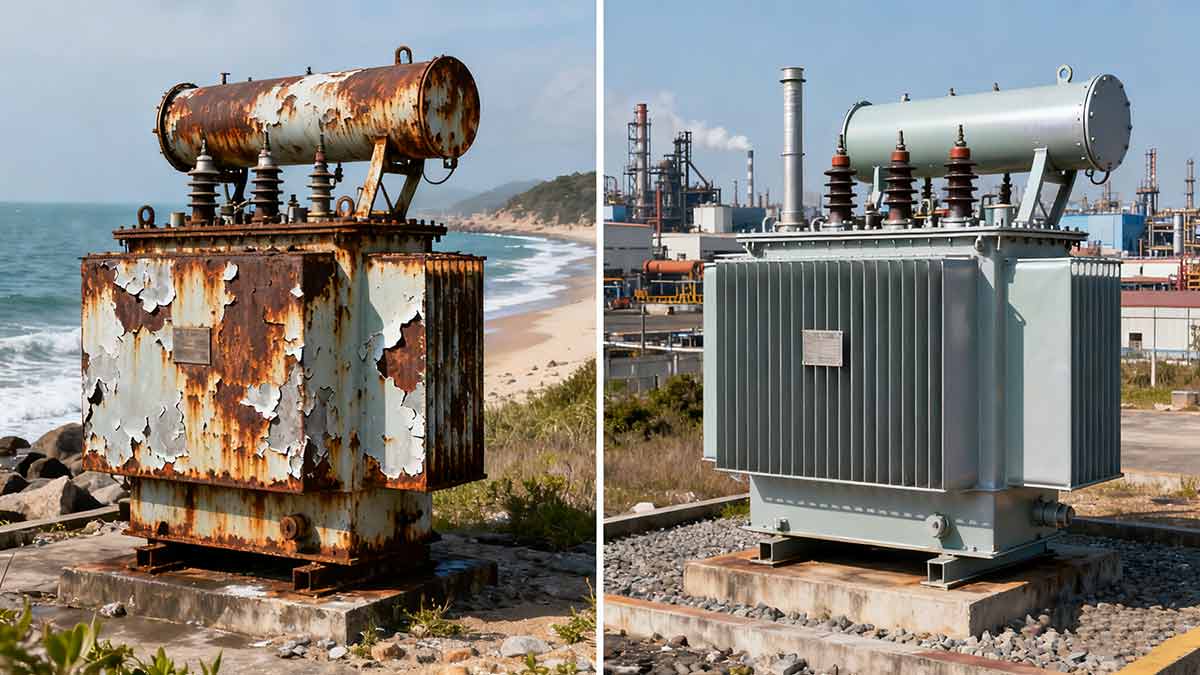
4 Failure #3: Corrosion & Weather Exposure
Power pole transformers endure rain, snow, salt spray, and industrial pollutants—making corrosion a silent killer. Lihe Transformer’s weather-resistant designs combat this, as 20% of transformer failures stem from rust, leaks, or material degradation.
Corrosion attacks transformer tanks, bushings, and connections, leading to oil leaks, structural weakness, and electrical faults. Lihe’s solutions are engineered for extreme environments—from coastal salt air to industrial smog.
Causes, Impacts & Lihe’s Weatherproofing
- Common Corrosion Triggers:
- Coastal Environments: Salt spray accelerates metal rust (Lihe’s marine-grade protection addresses this).
- Industrial Zones: Sulfur dioxide and dust corrode coatings (our epoxy finishes resist chemical attack).
- Temperature Fluctuations: Freeze-thaw cycles crack seals (Lihe’s EPDM gaskets remain flexible to -40°C).
- Critical Impacts:
- Oil Leaks: Loss of insulating oil leads to overheating (Lihe’s double-sealed tanks prevent this).
- Connection Failure: Corroded terminals increase resistance and generate heat.
- Structural Collapse: Rust weakens tanks (Lihe’s 3mm steel tanks with galvanization avoid this).
- Lihe’s Weather-Resistant Features:
- Corrosion-Resistant Materials: Hot-dip galvanized steel tanks + epoxy powder coating (resists 1,000 hours of salt spray testing).
- Sealed Design: IP67-rated enclosures prevent moisture ingress (ideal for humid regions).
- UV Protection: External coatings block UV radiation, preventing material degradation.
- Drainage Systems: Sloped tank tops and drain holes eliminate standing water.

| Protection Method | Lifespan in Harsh Environments | Cost-Benefit Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Galvanized + Epoxy Coating | 15–20 years | 3x longer life vs. standard paint |
| EPDM Seals | 10–15 years | Eliminates 90% of oil leak issues |
| IP67 Enclosure | 25+ years | No maintenance for moisture-related issues |
Lihe recently supplied transformers for a coastal community in California, where salt air had previously destroyed transformers in 5–7 years. Our marine-grade units (galvanized tanks + silicone bushings) have operated flawlessly for 8 years—with zero corrosion-related maintenance.
5 Failure #4: Overloading from Improper Sizing
Installing an undersized transformer is like trying to power a refrigerator with a phone charger—eventually, it fails. Overloading from improper sizing is responsible for 15% of power pole transformer failures, and Lihe Transformer’s precision sizing process eliminates this risk.

Overloading occurs when a transformer’s kVA rating can’t handle peak demand (e.g., a 50kVA unit powering a 75kVA load). This leads to chronic overheating, insulation breakdown, and shortened lifespan—issues Lihe avoids with data-driven sizing.
Why Improper Sizing Happens & Lihe’s Fix
- Root Causes of Oversizing/Undersizing:
- Underestimating Growth: Failing to account for new homes, EV chargers, or industrial expansion.
- Outdated Load Data: Using historical usage instead of modern consumption patterns (e.g., smart home devices).
- Ignoring Diversity Factors: Assuming all loads run simultaneously (Lihe’s analysis accounts for load diversity).
- Critical Impacts:
- Premature Aging: A 20% overload cuts transformer life by 50% (Lihe’s units include 10–25% growth buffers).
- Voltage Dips: Undersized units can’t maintain stable voltage during peak hours.
- Energy Waste: Oversized transformers have 30% higher core losses (Lihe’s right-sizing optimizes efficiency).
- Lihe’s Precision Sizing Process:
- Load Analysis: Our engineers calculate peak/average loads using smart metering data and 5-year growth projections.
- Diversity Factor Application: For residential areas, we use 0.2–0.4 (not all appliances run at once); 0.7–0.9 for industrial.
- Growth Buffers: Standard 10–25% extra capacity (customizable for fast-growing regions).
- Modular Designs: Lihe’s transformers allow easy capacity upgrades (e.g., 50kVA → 75kVA) without full replacement.
| Overload Percentage | Lihe Transformer Lifespan Impact | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| 10% (Continuous) | 50% lifespan reduction | Upgrade to next kVA rating |
| 20% (Continuous) | 75% lifespan reduction | Immediate replacement |
| 30%+ (Any Duration) | Catastrophic failure risk | Emergency load reduction + replacement |
A suburban utility recently approached Lihe after struggling with 6 annual transformer failures. We discovered their 50kVA units were powering 70kVA loads (due to EV charging growth). Lihe’s solution: right-size to 75kVA units with 20% growth buffers. Since installation, zero overloading failures have occurred.
6 Failure #5: Loose Connections & Poor Installation
A loose wire might seem trivial—but in a power pole transformer, it’s a disaster waiting to happen. Lihe Transformer’s strict installation standards address this, as 10% of failures stem from poor setup or vibration-induced loose connections.
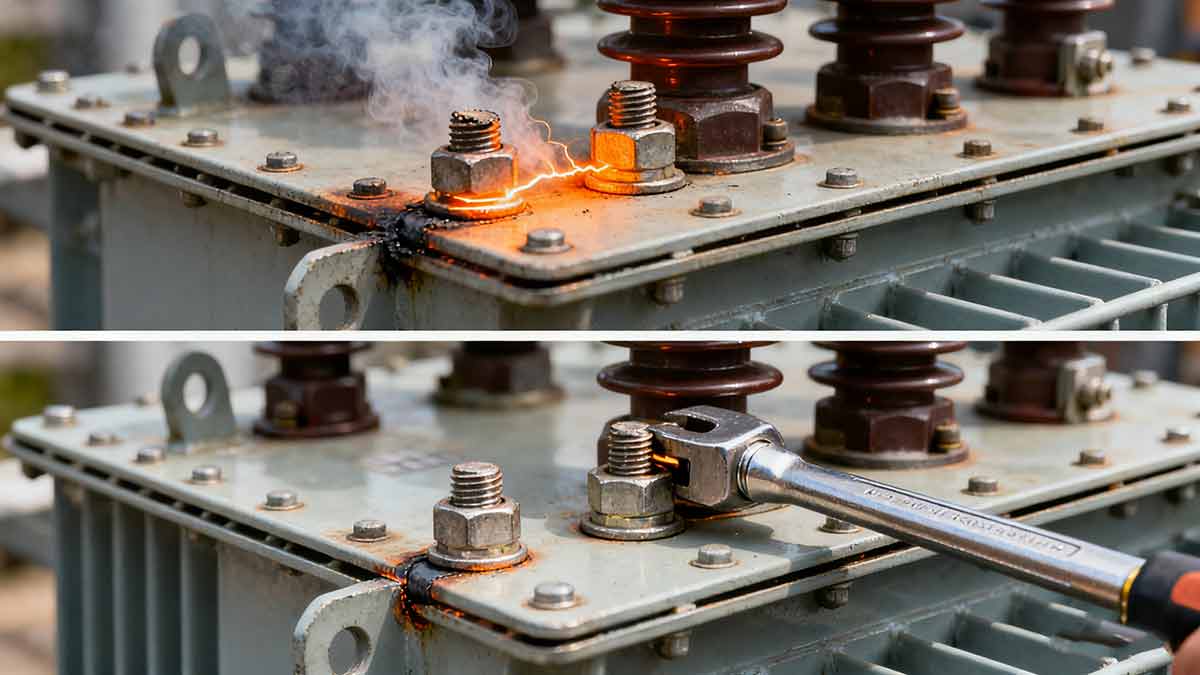
Loose connections increase electrical resistance, generating heat and arcing that damage terminals, bushings, and windings. Lihe’s installation protocols and durable components eliminate this risk.
Causes, Impacts & Lihe’s Installation Standards
- Common Connection Issues:
- Improper Torque: Under/over-tightened bolts (Lihe uses calibrated torque tools).
- Vibration: Wind or nearby equipment loosens connections (our lock washers and vibration dampeners prevent this).
- Corrosion: Oxidized terminals increase resistance (Lihe’s tinned copper connections resist rust).
- Critical Impacts:
- Arcing: Sparking between loose connections can ignite oil or cause fires.
- Oil Leaks: Loose tank bolts break seals (Lihe’s torque-spec bolts avoid this).
- Voltage Fluctuations: Intermittent connections cause flickering lights or equipment damage.
- Lihe’s Reliable Connection Solutions:
- Precision Installation: Factory-trained technicians use torque wrenches (40–50 Nm for bushings, 60–70 Nm for tank bolts).
- Locking Components: Nylon-insert lock nuts and spring washers prevent vibration loosening.
- Corrosion-Resistant Connections: Tinned copper terminals with anti-oxidant grease.
- Vibration Dampeners: Rubber mounts reduce movement (critical for windy or seismic regions).
| Connection Type | Lihe Recommended Torque | Consequence of Improper Torque |
|---|---|---|
| Bushing Terminals | 40–50 Nm | Arcing, overheating |
| Tank Bolts | 60–70 Nm | Oil leaks, structural weakness |
| Ground Connections | 20–30 Nm | Surge protection failure |
Lihe’s quality control team once rejected a batch of transformers after discovering a supplier’s loose bushing connections. Our strict testing (including thermal imaging and torque verification) ensures every unit leaves the factory with secure, reliable connections.
7 Preventive Maintenance Tips for Field Technicians (Lihe Approved)
Proper maintenance extends Lihe Transformer’s lifespan by 50%—here’s our field-tested checklist for technicians:

1. Monthly Visual Inspections
- Check for oil leaks (Lihe’s sight glasses simplify level verification).
- Inspect bushings for cracks, contamination, or discoloration.
- Verify connections are tight and corrosion-free.
- Clear debris from cooling fins (dust blocks heat dissipation).
2. Quarterly Thermal Imaging
- Use infrared cameras to detect hot spots (target: <105°C operating temp).
- Focus on terminals, bushings, and radiator fins.
- Compare readings to Lihe’s baseline data (provided with each unit).
3. Annual Oil Testing
- Perform dissolved gas analysis (DGA) to detect internal faults.
- Test dielectric strength (Lihe recommends >25 kV for safe operation).
- Monitor moisture content (<10 ppm is ideal).
4. Bi-Annual Electrical Testing
- Measure insulation resistance (Lihe’s transformers should maintain >100 MΩ).
- Check turns ratio and winding resistance.
- Verify surge arrester functionality.
5. Annual Mechanical Maintenance
- Retighten connections to Lihe’s torque specs.
- Lubricate tap changers (if applicable).
- Inspect and replace worn gaskets/seals.
Lihe offers a free maintenance training program for technicians—contact our team to schedule a session.

8 When to Repair vs. Replace: Lihe’s Cost-Benefit Guide
Deciding whether to repair or replace a transformer is critical—Lihe’s framework helps you make the right call:
Key Decision Factors
| Factor | Repair (Recommended) | Replace (Recommended) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | <10 years old with minor issues | >15 years old or major damage |
| Repair Cost | <30% of replacement cost | >30% of replacement cost |
| Efficiency | Lihe high-efficiency model (98%+) | Outdated model (≤95% efficiency) |
| Future Growth | Sufficient capacity for 5+ years | Already undersized or no growth room |
| Safety/Reliability | Minor issues (e.g., small oil leak) | Major faults (e.g., winding damage, corrosion) |
Lihe’s Replacement Advantage
- New units include a 10-year warranty (vs. typical 1–2 years for repairs).
- 30% higher efficiency reduces energy costs by $1,500–$3,000 annually.
- Smart monitoring integration (optional) enables predictive maintenance.
A utility recently saved $40,000 over 5 years by replacing a 20-year-old transformer (repair cost: $15,000) with Lihe’s 75kVA unit ($35,000). The energy savings and reduced maintenance more than offset the upfront cost.
9 Conclusion
Power pole transformer failures don’t have to be inevitable—with Lihe Transformer’s durable designs, precision sizing, and proactive maintenance, you can minimize downtime and maximize reliability. By addressing the top 5 failures (thermal overload, surge damage, corrosion, improper sizing, and loose connections), you’ll build a more resilient grid that serves communities for decades.

Lihe Transformer’s power pole units are engineered to withstand harsh environments, handle modern loads (EVs, smart homes), and integrate with smart grid technologies. Whether you’re replacing aging equipment or planning a new installation, our team provides end-to-end support—from sizing to installation to maintenance.
Ready to enhance your grid’s reliability? Contact Lihe Transformer today for a custom solution tailored to your needs.
