Difference Between Dry And Oil Type Transformer
Dry-type transformers and oil-immersed transformers differ significantly in structure, performance, and application scenarios; the specific differences are as follows:
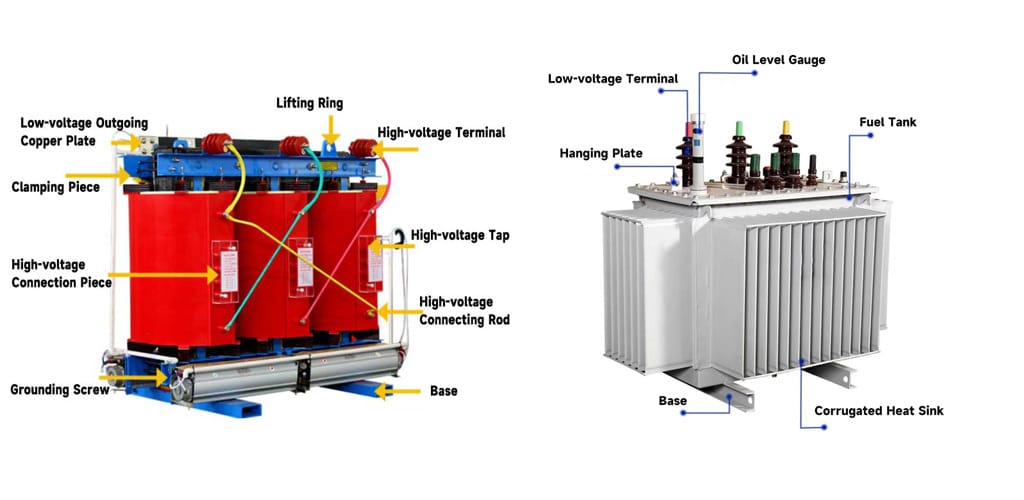
Structural Comparison
Item | Dry-type Transformer | Oil-immersed Transformer |
Insulation Materials | Solid insulation materials such as air, epoxy resin casting, and vacuum pressure impregnation (VPI) | Transformer oil (mineral oil or synthetic ester oil, which serves both insulation and cooling functions) |
Cooling Method | Natural air cooling (AN) or forced air cooling (AF) | Oil circulation heat dissipation (e.g., natural oil cooling ONAN, forced oil circulation air cooling OFAF) |
Windings | Copper/aluminum windings with outer layers wrapped in epoxy resin or Nomex paper, featuring high protection levels | Copper/aluminum windings directly immersed in insulating oil |
Enclosure & Accessories | Typically IP20 protection level; optional dustproof and waterproof enclosures (e.g., IP54) | Sealed oil tank, equipped with accessories such as oil conservators (oil pillows), pressure relief valves, and oil level gauges |
Differences in Working Principles
Common principle: Both are based on electromagnetic induction, achieving voltage transformation through the turn ratio of windings.
Core differences:
- Heat dissipation: Dry-type transformers rely on air convection or forced air cooling; oil-immersed transformers transfer heat to radiators/coolers via oil circulation.
- Insulation: Dry-type transformers depend on solid material insulation; oil-immersed transformers utilize the high insulation and heat capacity of liquid oil.

Comparison of Performance Characteristics
Characteristic | Dry-type Transformer | Oil-immersed Transformer |
Safety | Oil-free, no fire or leakage risks; suitable for places with high fire protection requirements | Oil is flammable, requiring additional fire prevention measures; risk of oil leakage pollution exists |
Heat Dissipation Capacity | Poor; capacity usually ≤ 2500kVA | Excellent; capacity can reach hundreds of MVA, suitable for high-load scenarios |
Environmental Friendliness | No hidden danger of oil leakage; more environmentally friendly | Requires waste oil disposal; risk of leakage pollution |
Volume & Weight | Smaller volume and lighter weight (no need for oil tanks or oil circulation devices) | Larger volume and heavier weight (including oil tanks, radiators, etc.) |
Noise Level | Lower (no noise from oil circulation equipment) | Higher (noise generated by operating oil pumps and fans) |
Maintenance Cost | Maintenance-free or low maintenance (no need for oil replacement or oil quality inspection) | Requires regular oil quality and level inspections; complex maintenance |
Application Scenarios
Dry-type Transformers | Oil-immersed Transformers |
Indoor scenarios: high-rise buildings, subways, hospitals, data centers (high fire protection requirements) | Large-capacity scenarios: main transformers in substations, industrial parks (e.g., steel, chemical industries) |
Special environments: humid, dusty environments (adaptable with IP54 protection) | Outdoor applications: power grid transmission/distribution lines, power plant step-up stations |
Distributed energy: wind farms, photovoltaic power stations (medium and low-voltage distribution sides) | High-temperature environments: scenarios requiring long-term high-load operation (oil has high heat dissipation efficiency) |
Summary of Advantages and Disadvantages
Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
Dry-type Transformer | Safe and environmentally friendly (oil-free), maintenance-free, flexible installation, low noise | Limited capacity, high cost, poor heat dissipation, shorter service life |
Oil-immersed Transformer | Large capacity, low cost, good heat dissipation, long service life | Fire risk exists, complex maintenance, large volume, poor environmental friendliness (oil leakage/waste oil) |
Selection Suggestions
- Choose dry-type transformers for scenarios with high fire protection requirements (e.g., urban centers, hospitals), limited space, or high environmental sensitivity.
- Choose oil-immersed transformers for scenarios with large capacity requirements (e.g., industrial zones), outdoor installation, or cost sensitivity (e.g., rural power grids).

