What are dry type transformers?
In power transmission and distribution systems, transformers play a crucial role, and dry-type transformers, as an important member, are widely used in various places due to their advantages of safety, environmental protection, and convenient maintenance. This article will delve into the principles and structure of dry-type transformers to help everyone better understand this key power equipment.
Basic Concepts of Dry-Type Transformers
A dry-type transformer is a type of transformer where the iron core and windings are not immersed in insulating liquid but are cooled by air. Compared with oil-immersed transformers, it does not require an oil tank or insulating oil, has the characteristics of small size, light weight, and easy installation, and can operate stably under relatively harsh environmental conditions, such as high-rise buildings, commercial centers, hospitals, subways, and other places with high fire protection requirements.
Working Principles of Dry-Type Transformers
(1) Basis of the Electromagnetic Induction Principle
The working principle of a dry-type transformer is based on the law of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current is applied to the primary winding, an alternating magnetic flux is generated in the iron core. According to the law of electromagnetic induction, the alternating magnetic flux passes through the secondary winding, inducing an electromotive force in the secondary winding.
(2) Voltage Transformation Process
If the number of turns of the primary winding is N1, the number of turns of the secondary winding is N2, the primary side voltage is U1, and the secondary side voltage is U2, under ideal conditions, the voltage is proportional to the number of turns, that is, U1/U2 = N1/N2. By changing the turns ratio of the primary and secondary windings, voltage can be increased or decreased to meet different electricity needs.
(3) Energy Transfer Mode
In the process of energy transfer, the primary winding absorbs electrical energy from the power source, converts the electrical energy into magnetic energy through electromagnetic induction, and stores it in the iron core. And then the magnetic energy is converted into electrical energy and output in the secondary winding, realizing the transfer of electrical energy. In an ideal state, the input power is equal to the output power.
Structural Composition of Dry-Type Transformers
(1) Iron Core
The iron core is the magnetic circuit part of the dry-type transformer, and its main function is to conduct magnetism, reduce magnetic resistance, and eddy current loss. The iron core is usually made of stacked silicon steel sheets with high magnetic permeability, and the surface of the silicon steel sheets is coated with insulating paint to reduce eddy current loss.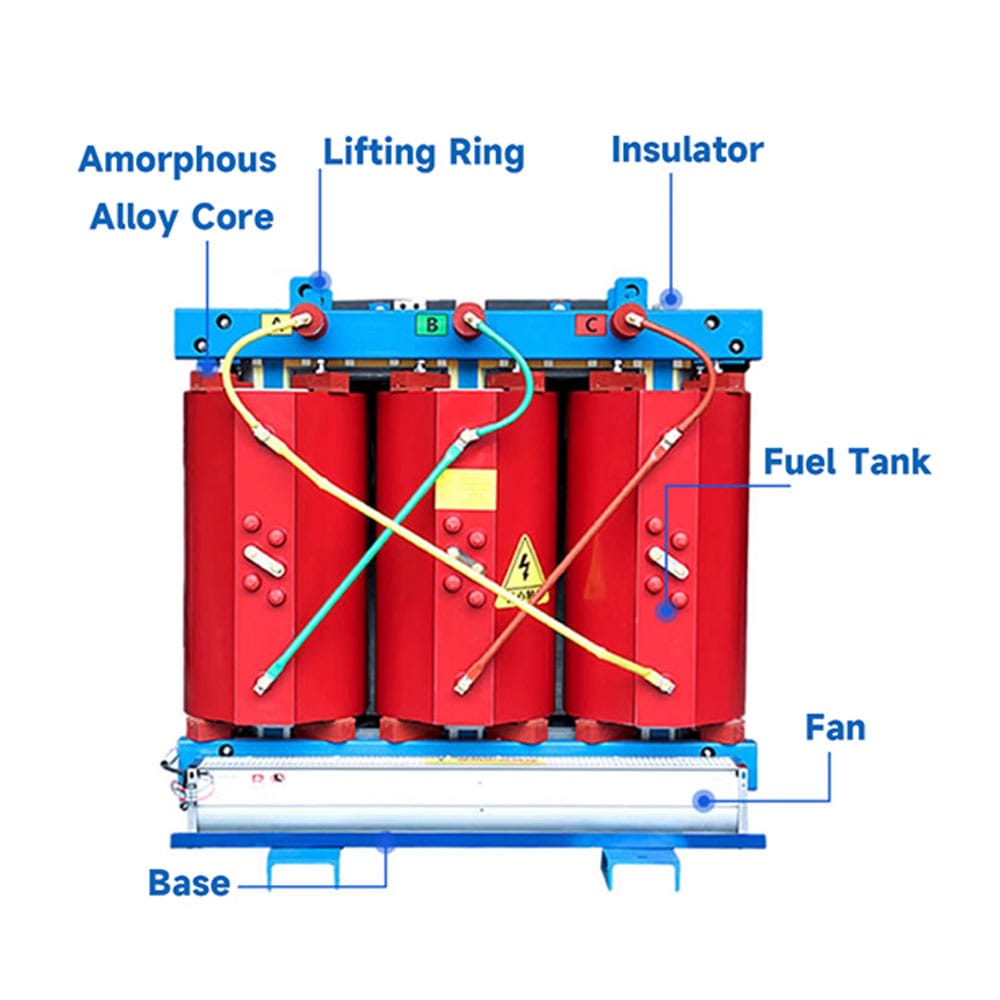
The structure of the iron core has two types: core type and shell type. The core type iron core has a simple structure and is convenient to manufacture, so it is widely used; the shell type iron core has high mechanical strength and is suitable for large-capacity transformers.
(2) Windings
Windings are the circuit part of dry-type transformers, responsible for current conduction and voltage transformation. Windings are generally made of copper or aluminum wires, and the surface of the wires is wrapped with insulating materials, such as polyimide film, epoxy resin, etc., to ensure insulation between windings and between windings and iron cores.
According to the arrangement of windings, they can be divided into concentric windings and overlapping windings. Concentric windings have a simple structure and are easy to manufacture, so they are widely used; overlapping windings have good insulation performance and high mechanical strength, and are suitable for high-voltage and large-capacity transformers.
(3) Cooling System
Since dry-type transformers rely on air cooling, their cooling systems are relatively simple. It mainly includes two methods: natural air cooling and forced air cooling. Natural air cooling uses natural convection of air for heat dissipation, which is suitable for small-capacity transformers; forced air cooling uses fans to force air flow to enhance the heat dissipation effect, which is suitable for large-capacity transformers. The good operation of the cooling system can ensure that the transformer operates stably at normal working temperature.
(4) Insulation Structure
The insulation structure is the key to ensuring the safe operation of dry-type transformers. In addition to the insulating materials on the surface of the winding wires, it also includes insulation between windings, between windings and iron cores, and between windings and shells.
Commonly used insulating materials include insulating paper, insulating cardboard, epoxy resin, etc. These insulating materials have good insulation performance and heat resistance, and can withstand the voltage and temperature during the operation of the transformer.
(5) Shell
The shell mainly plays a role in protecting the internal components of the transformer, preventing dust and debris from entering the transformer, and also has a certain heat dissipation and sound insulation effect.
The shell is usually made of a steel plate or an aluminum alloy plate, and the surface is anti-corrosion treated to improve its service life. The design of the shell should also consider the needs of ventilation and heat dissipation to ensure that the cooling air can circulate smoothly.
Advantages and Application Scenarios of Dry-Type Transformers
(1) Advantages
Dry-type transformers have the characteristics of no oil and good fire resistance, and will not cause fire accidents due to oil leakage, so they have high safety; they are easy to maintain, do not need to regularly check oil level, oil quality, etc., reducing maintenance workload and cost; they are small in size, light in weight, flexible in installation, and can save installation space; they are suitable for various harsh environments, such as humid, dusty, high-temperature places.
(2) Application Scenarios
Based on the above advantages, dry-type transformers are widely used in power distribution systems of high-rise buildings, commercial centers, hospitals, schools, subways, airports, industrial enterprises, and other places, and can also be used in power conversion in new energy power generation, rail transit, and other fields.
To sum up, dry-type transformers work based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, and their structure is composed of iron core, windings, cooling system, insulation structure and shell. Understanding the principle and structure of dry-type transformers helps us better select, use and maintain this important power equipment, and ensure the safe and stable operation of the power system.
Simply put, a dry-type transformer refers to a transformer whose iron core and windings are not immersed in insulating oil.
Dry-type transformers use the principle of electromagnetic induction to transmit power and signals from one circuit to another, which are important factors in power transmission and signal transmission. Its working principle is the same as that of other transformers, following the physical principle of electromagnetic coupling. Due to the mutual inductance between the two circuits, the current change in one circuit affects the other circuit through mutual inductance. There is close cooperation and mutual influence between the input and output of two or more circuit components or electrical networks, and energy is transmitted from one side to the other through interaction.
The structure type of dry-type transformer is mainly composed of an iron core made of silicon steel sheets and a coil cast with epoxy resin. An insulating cylinder is placed between the high-voltage and low-voltage coils to increase electrical insulation, and the coils are supported and restrained by pads. The fasteners for overlapping parts have anti-loosening performance.
There are three forms of dry-type transformers.
- Open type: It is a commonly used form. Its body is in direct contact with the atmosphere and is suitable for relatively dry and clean rooms (when the ambient temperature is 20 degrees, the relative humidity should not exceed 85%). Generally, there are two cooling methods: air self-cooling and air cooling.
- Closed type: The body is in a closed shell and not in direct contact with the atmosphere (due to poor sealing and heat dissipation conditions, it is mainly used in mines and is explosion-proof).
- Cast type: Epoxy resin or other resins are used for casting as the main insulation. It has a simple structure and small volume, and is suitable for transformers with small capacity.
Characteristics and Structure of Dry-Type Transformers
1. Temperature control system
The safe operation and service life of dry-type transformers largely depend on the safety and reliability of the transformer winding insulation.
2. Cooling method
The cooling methods of dry-type transformers are divided into natural air cooling (AN) and forced air cooling (AF). When naturally air-cooled, the transformer can operate continuously for a long time under rated capacity. When forced air cooling is used, the output capacity of the transformer can be increased by 50%.
It is suitable for intermittent overload operation or emergency accident overload operation; because the load loss and impedance voltage increase greatly during overload, it is in a non-economic operation state, so it should not be in long-term continuous overload operation.
Dry-type transformers and oil-immersed transformers are the two most commonly used transformers. Compared with oil-immersed transformers, dry-type transformers have good fire resistance and are often used in hospitals, airports, stations, and other places with high fire protection requirements, but their price is relatively high, and they also have certain requirements for the environment. For example, it should not be too humid, and there should not be too much dust and dirt. In addition, the operational maturity of dry-type transformers is not as good as that of oil-immersed transformers.
