What are the types of distribution transformers?
As important equipment in the power system, distribution transformers are widely used in various fields such as industry, commerce, and residential areas to ensure the stable supply of electricity.
So, what are the types of distribution transformers, and what are the differences in their applications? Today, we will help you gain an in-depth understanding of various types of distribution transformers.
According to different classification standards, distribution transformers can be divided into different types, such as those based on main insulation medium, phase number, voltage regulation mode, and structure and function. Each type of transformer has its specific application scenarios and technical advantages.

Classification by Main Insulation Medium: Oil-immersed vs. Dry-type Distribution Transformers
According to the main insulation medium, distribution transformers can be divided into three types: oil-immersed transformers, dry-type transformers, and gas-insulated transformers.
Oil-immersed Distribution Transformers
Oil-immersed distribution transformers cool down by immersing the iron core and windings in insulating oil, utilizing the heat dissipation performance of the insulating oil. They have good insulation and heat dissipation effects and are suitable for most industrial and commercial places.
For example, mineral oil distribution transformers and natural ester oil distribution transformers. Natural ester oil distribution transformers are more environmentally friendly than mineral oil transformers, with higher ignition points and better biodegradability, making them suitable for environments with higher fire protection requirements.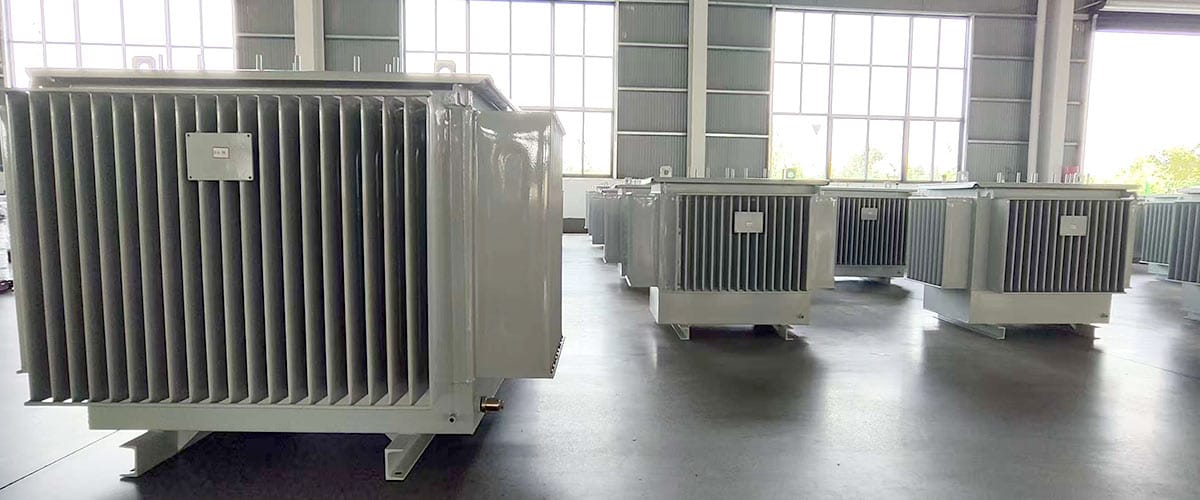
According to the type of casing, oil-immersed transformers can be further divided into the following categories:
- Non-closed oil-immersed transformers: Series products such as S8, S9, and S10 are widely used in industrial and mining enterprises, agriculture, and civil buildings.
- Closed oil-immersed transformers: Typical series include S9, S9-M, and S10-M. Due to their good sealing performance, they are mostly used in places with a lot of oil stains and chemical substances, such as the petroleum and chemical industries.
- Sealed oil-immersed transformers: Products such as BS9, S9-, S10-, S11-MR, SH, and SH12-M series can be widely used in power distribution in various places such as industrial and mining enterprises, agriculture, and civil buildings.
However, oil-immersed transformers also have some disadvantages, such as the risk of oil leakage during operation, which may cause fire hazards.
Dry-type Distribution Transformers
Dry-type distribution transformers do not use insulating liquids. Instead, they use materials such as epoxy resin for insulation and rely on natural air cooling for heat dissipation. They are suitable for places with high requirements for fire and moisture resistance. They have a simple structure and are easy to maintain, and are commonly found in high-rise buildings or areas with dense equipment.
Dry-type transformers can be divided by insulation medium into:
- Encapsulated coil dry-type transformers: Series products such as SCB8, SC (B) 9, SC (B) 10, and SCR-10 are suitable for places with high fire protection requirements, such as high-rise buildings, commercial centers, airports, stations, subways, hospitals, and factories.
- Non-encapsulated coil dry-type transformers: Represented by series products such as SG10, they are also suitable for high-rise buildings, commercial centers, airports, stations, subways, petrochemical industries, and other places.
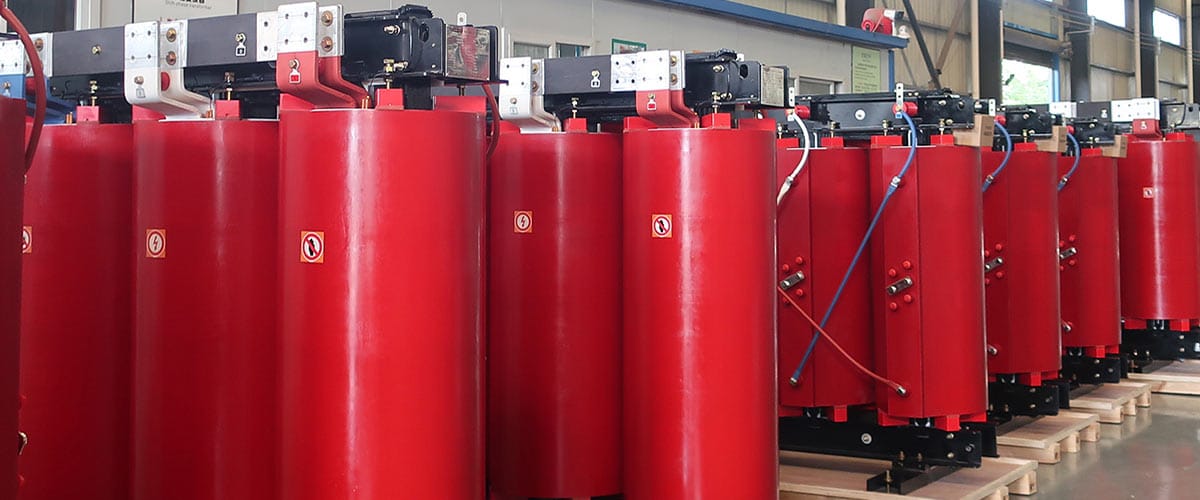

The advantages of dry-type transformers also include high working voltage, large capacity, high insulation strength, strong short-circuit resistance, environmental friendliness and easy recycling, low operating noise, small size, light weight, convenient installation, and debugging. They can be installed in the center of the load, without the need for a special foundation, and without a separate transformer room or core lifting maintenance, which can save floor space.
Gas-insulated Distribution Transformers
Gas-insulated transformers are a new type of disaster-prevention transformer, mainly used to meet the needs of power supply quality and reduce line losses. They are usually installed on the ground floor of high-rise buildings to bring power transformation equipment closer to users. This type of transformer has good fire and explosion-proof properties, and can adapt to high humidity and dusty environmental conditions. Its manufacturing technology has matured after 30 years of development and has now achieved commercial mass production.
Gas-insulated transformers are divided into dry and wet types. The dry type uses SF6 gas as the insulation and cooling medium; the wet type mainly uses SF6 gas as the insulation medium and liquid-gas two-phase fluorides (such as FC-75 (C8F16O), Freon R-113 (C2Cl3F3)) as the cooling medium, which cools the transformer through changes in the state of the substance.
Its advantages include excellent fire and explosion-proof performance (SF6 gas is non-flammable and has high stability, and solid and liquid materials are also non-flammable), resistance to humid environments (the interior of the transformer is sealed and not affected by external moisture, dampness, and dust), low maintenance (the interior is sealed, insulation materials are not easy to deteriorate, and no complex oil treatment and maintenance work is required), small floor space and light weight (SF6 gas has excellent insulation and heat dissipation performance), and a wide range of applications (suitable for various environments, especially large-scale projects and ultra-high voltage fields).
Classification by Phase Number: Single-phase Distribution Transformers and Three-phase Distribution Transformers
Single-phase distribution transformers are mainly used in low-voltage distribution networks and are suitable for single-phase loads. They are mainly used in homes or small commercial places. They have a simple structure, small size, low loss, and are very commonly used.
For industrial electricity or places that require three-phase electricity, three-phase distribution transformers are undoubtedly more suitable. They can support larger loads and are applicable to places with large-scale power demand, such as factories, commercial buildings, and power grid transmission.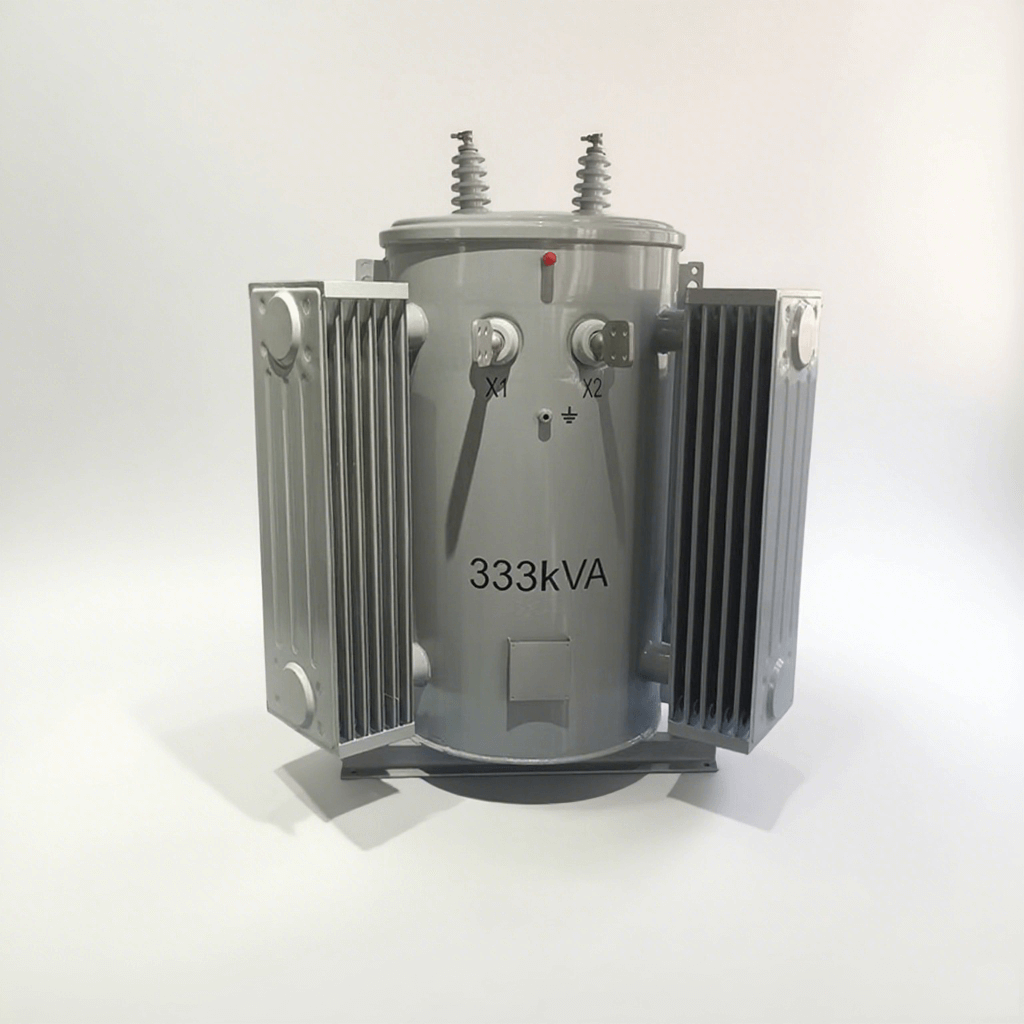
Three-phase distribution transformers have various connection methods, including delta, star, etc. Different connection methods can meet different power needs.
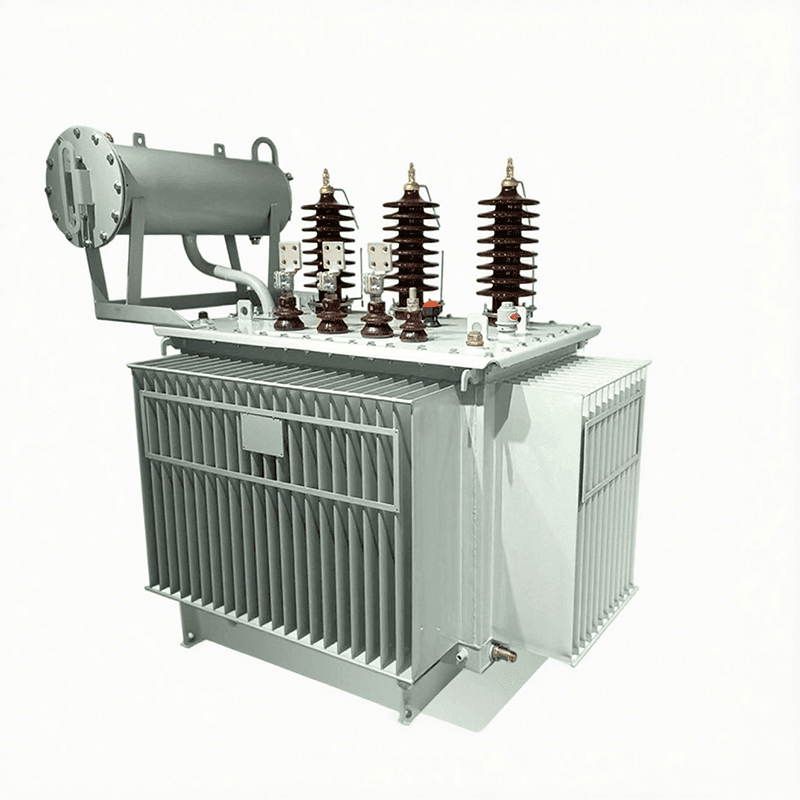
Classification by Voltage Regulation Mode: On-load Voltage Regulation Distribution Transformer vs. Off-load Voltage Regulation Distribution Transformer
On-load voltage regulation distribution transformers are equipment with tap changers, which can adjust the taps under load operation to achieve voltage regulation.
This type of distribution transformer is very suitable for places with large load changes and high requirements for voltage stability, such as places with large industrial equipment and high-rise buildings.
In contrast, off-load voltage regulation distribution transformers need to be adjusted when power is cut off; that is, they can only be adjusted when there is no load.
Although the operation is relatively troublesome, its structure is simpler and the cost is lower, so it is suitable for occasions where the load changes little.
Classification by Structure and Function: Special-purpose Distribution Transformers
With the development of technology, distribution transformers have shown more diversified applications in some specific scenarios.
For example, oil-immersed distribution transformers for wind power are specially used in wind farms to boost and transmit the electric energy generated by wind turbines. This type of transformer not only needs to adapt to harsh environments but also has strong impact resistance.
In addition, underground distribution transformers are often used in urban residential areas or commercial centers. They occupy less land, have high safety, can effectively save space, and have better coordination with the surrounding environment.
Mining distribution transformers are specially designed for special environments such as coal mines and metal mines. They have multiple characteristics, such as explosion-proof, moisture-proof, and dust-proof, to ensure stable operation in harsh environments.
Combined and Integrated Distribution Transformers
Combined distribution transformers integrate transformers, switchgear, fuses, and other supporting facilities into one device, which reduces the floor space and improves the convenience of installation and maintenance.
This type of distribution transformer is mostly used in places with high space requirements, such as high-rise buildings and residential communities.
Integrated distribution transformers combine high-voltage modules, transformer modules, low-voltage distribution modules, and other components into a compact whole.
This not only reduces the floor space but also improves the reliability and operating efficiency of the power supply. It is a common choice in urban distribution network transformation and new construction projects.
After learning about the various types of distribution transformers, do you have a deeper understanding of this large family?
Whether it is oil-immersed or dry-type, single-phase or three-phase, each type of distribution transformer has its unique advantages and application scenarios.
Choosing the right transformer according to specific needs can greatly improve the stability and safety of the power supply.
Summary: Core Differences and Selection Logic of Various Transformers
| Type | Core Advantages | Typical Application Scenarios | Limiting Conditions |
| Oil-immersed | Low cost, large capacity | Industrial and mining enterprises, rural power grids | Low fire protection requirements, need for maintenance |
| Dry-type | Fire and explosion proof, simple maintenance | High-rise buildings, hospitals, and subways | Capacity ≤ 2500kVA, high cost |
| Gas-insulated | Extreme fire resistance, resistance to harsh environments | Super high-rises, high humidity / dusty places | High cost, high technical threshold |
| Single-phase / Three-phase | Adapt to single-phase / three-phase loads | Homes/industry | Capacity matches the phase number |
| On-load / Off-load voltage regulation | Voltage stability / low cost | Large factories / residential areas | Degree of load fluctuation |
The following factors should be comprehensively considered when selecting: fire protection level, capacity requirements, environmental conditions (humidity, dust), maintenance costs, and voltage stability requirements.
